GUNT DigiSkills 5
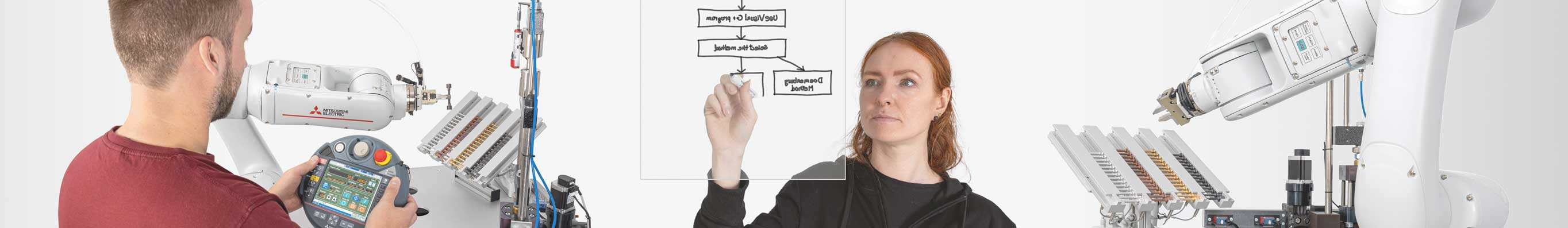
Robotics and automation - using materials testing as an example
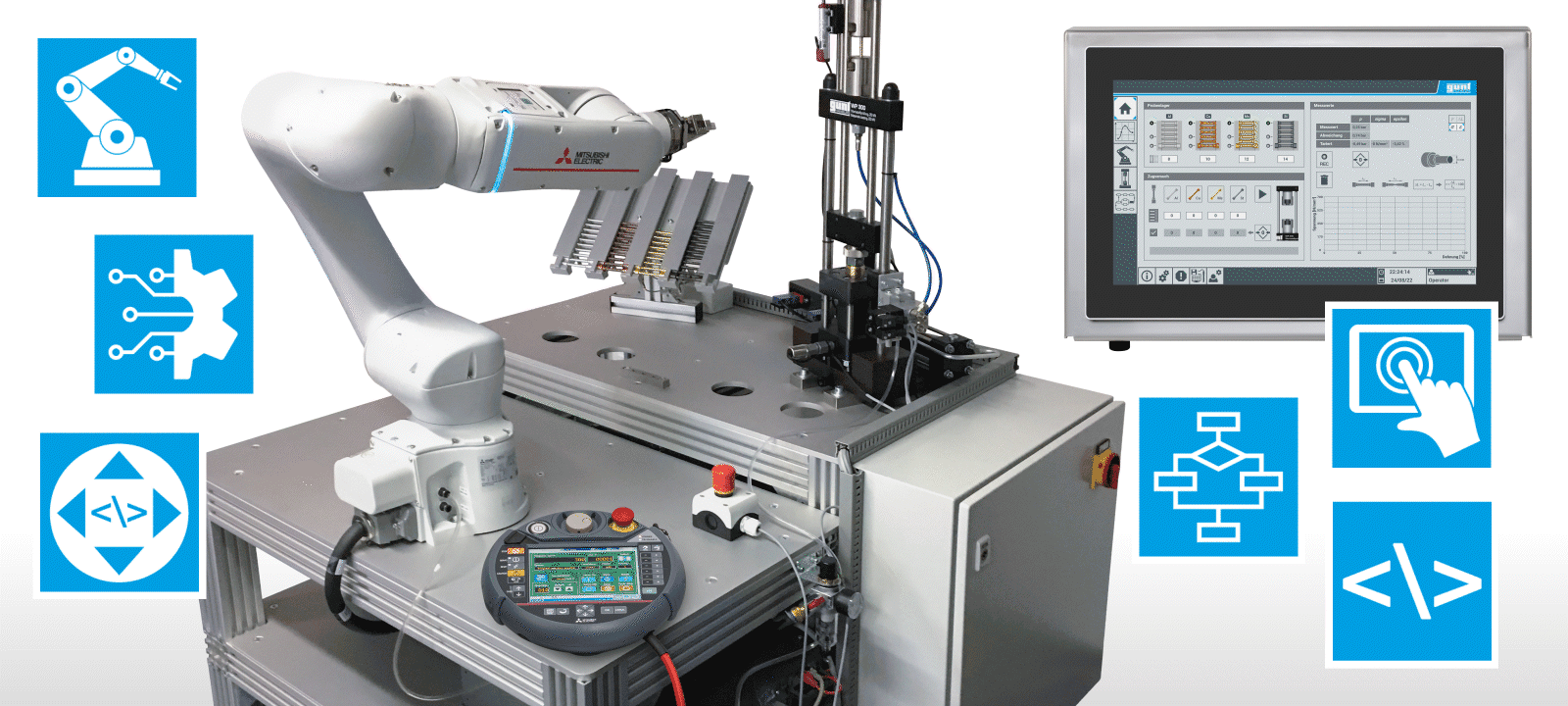
Automated process in quality inspection
Cobots are used in fields such as machine loading and quality inspection. Their use is based on process automation.
The DigiSkills 5 learning project sets out to automate processes for a mechanical testing procedure. Automation is explained step by step and underpinned with practical tasks, instructions and information.
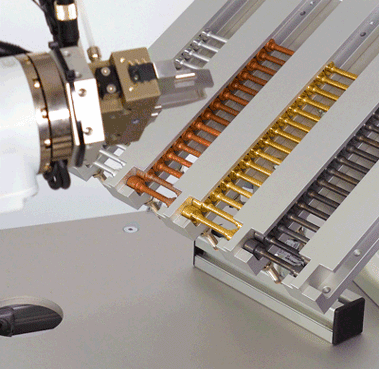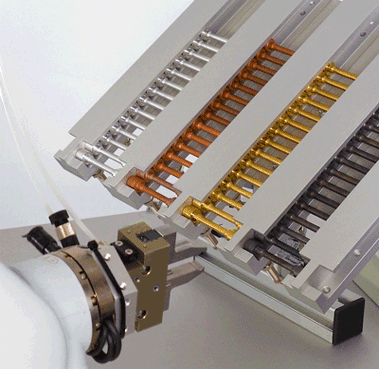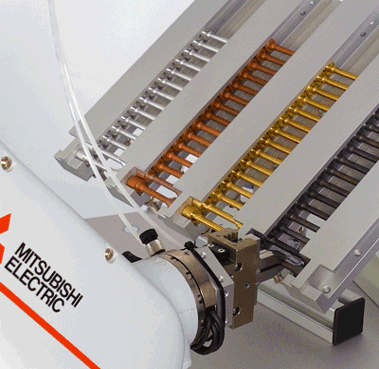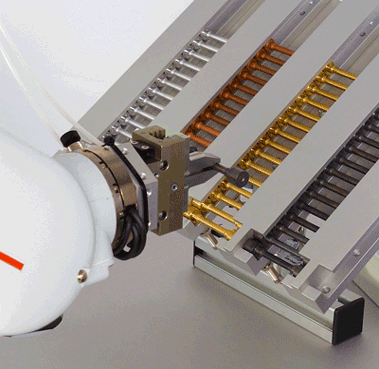
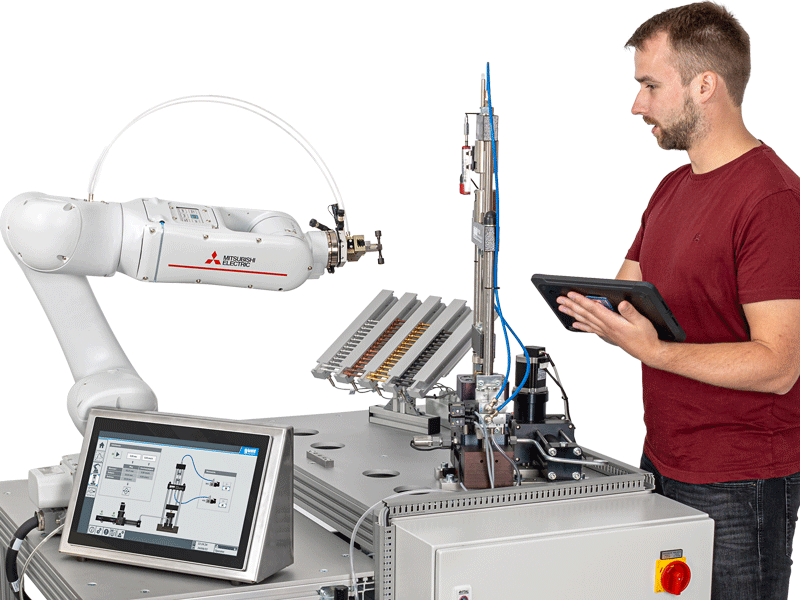
 Cobot
Cobot
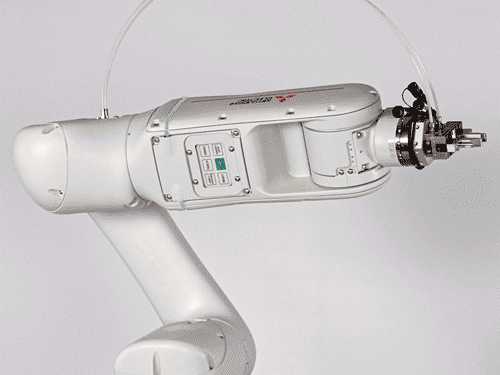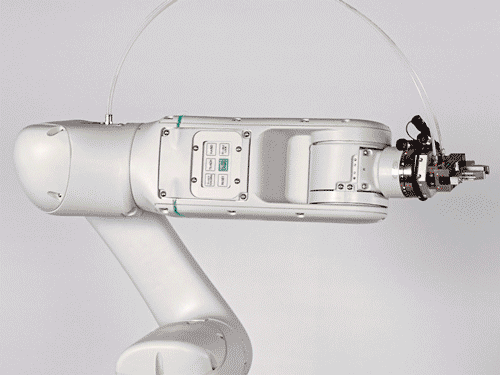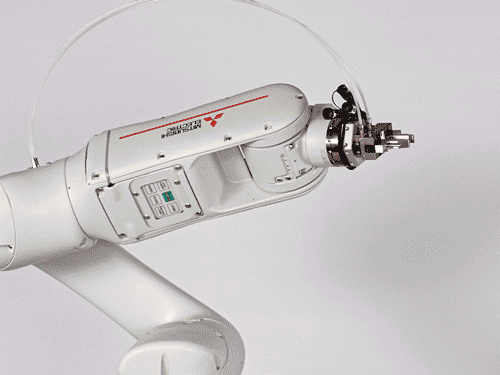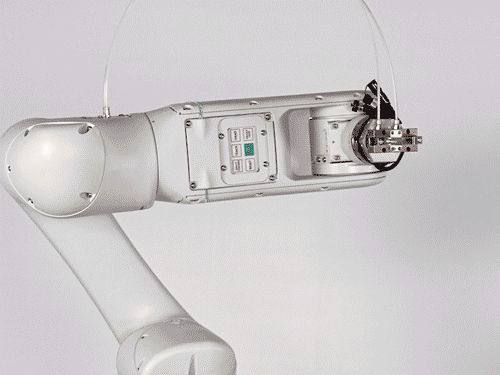
High-quality collaborative robot with industrial control for 6 axes
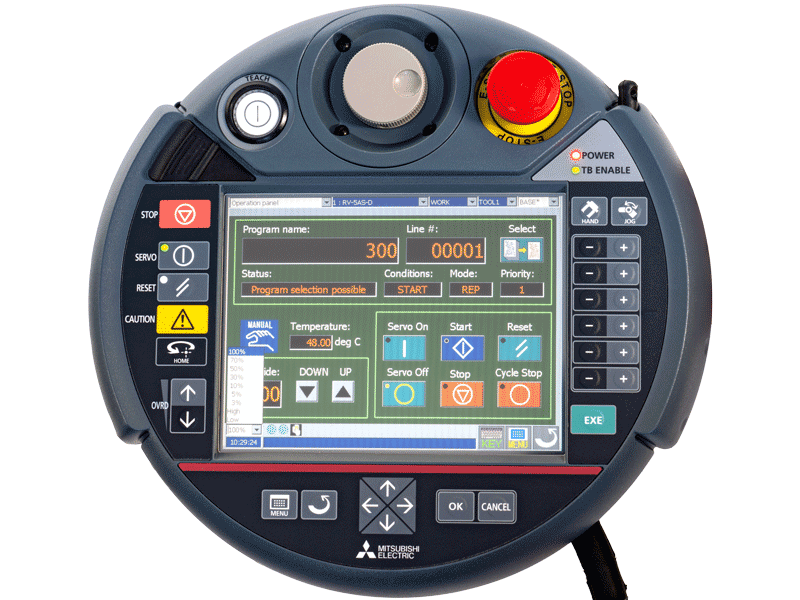
 Control element (HMI)
Control element (HMI)
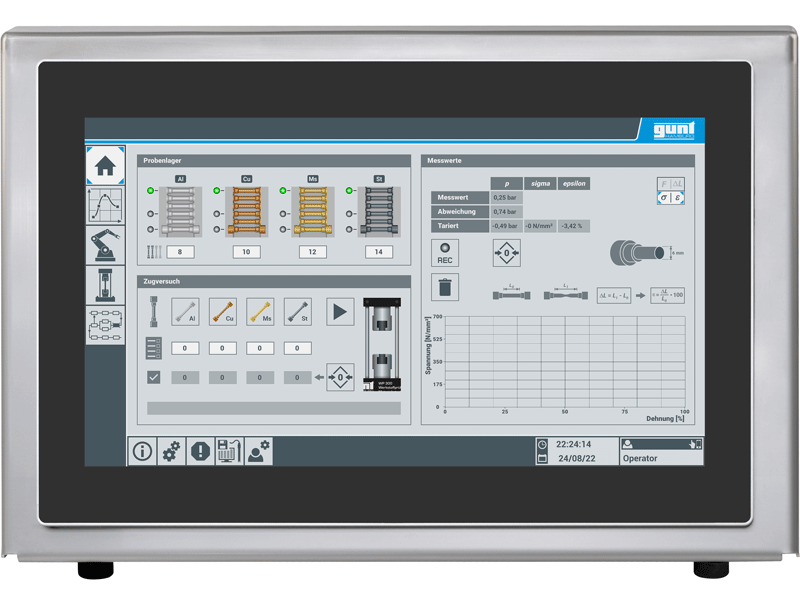
Freely movable control element (HMI Human Machine Interface) in separate housing with touch screen
 Process flow
Process flow
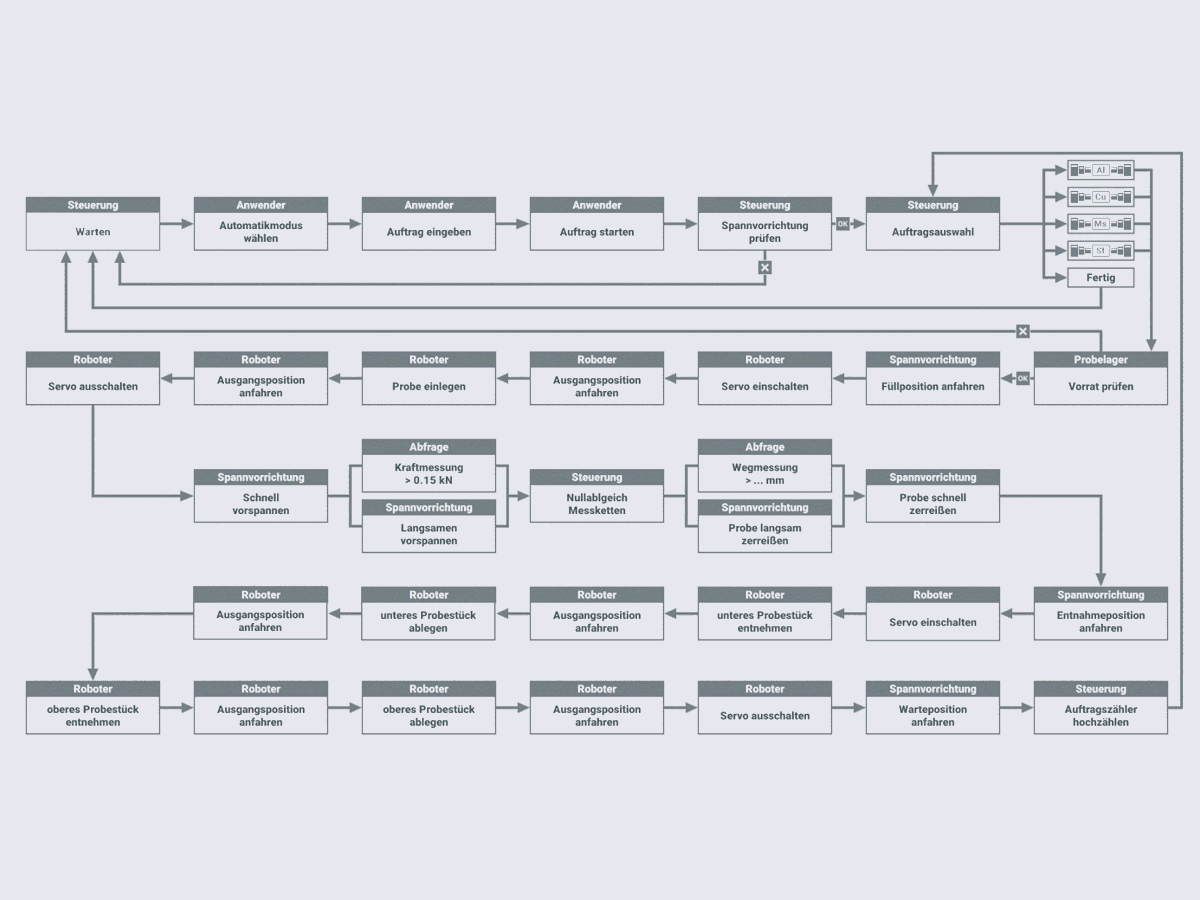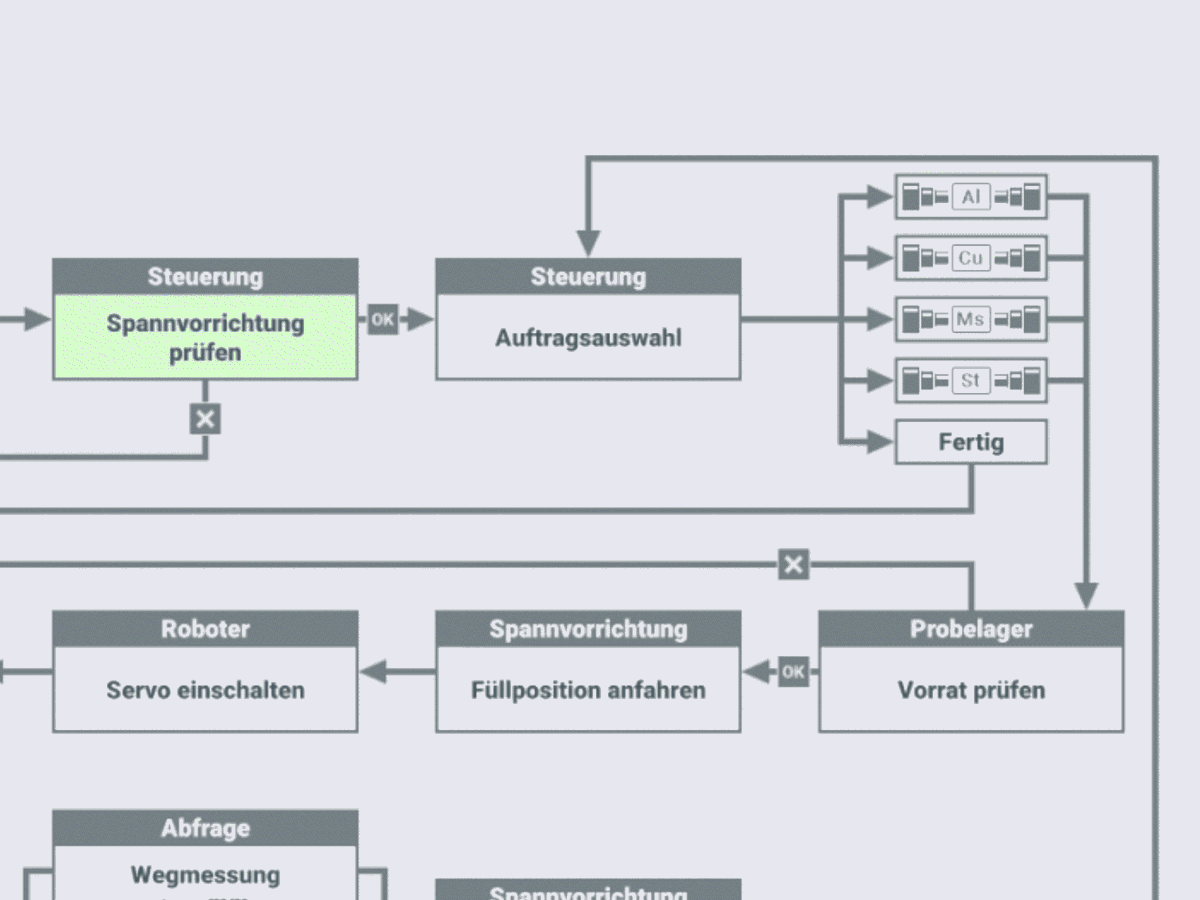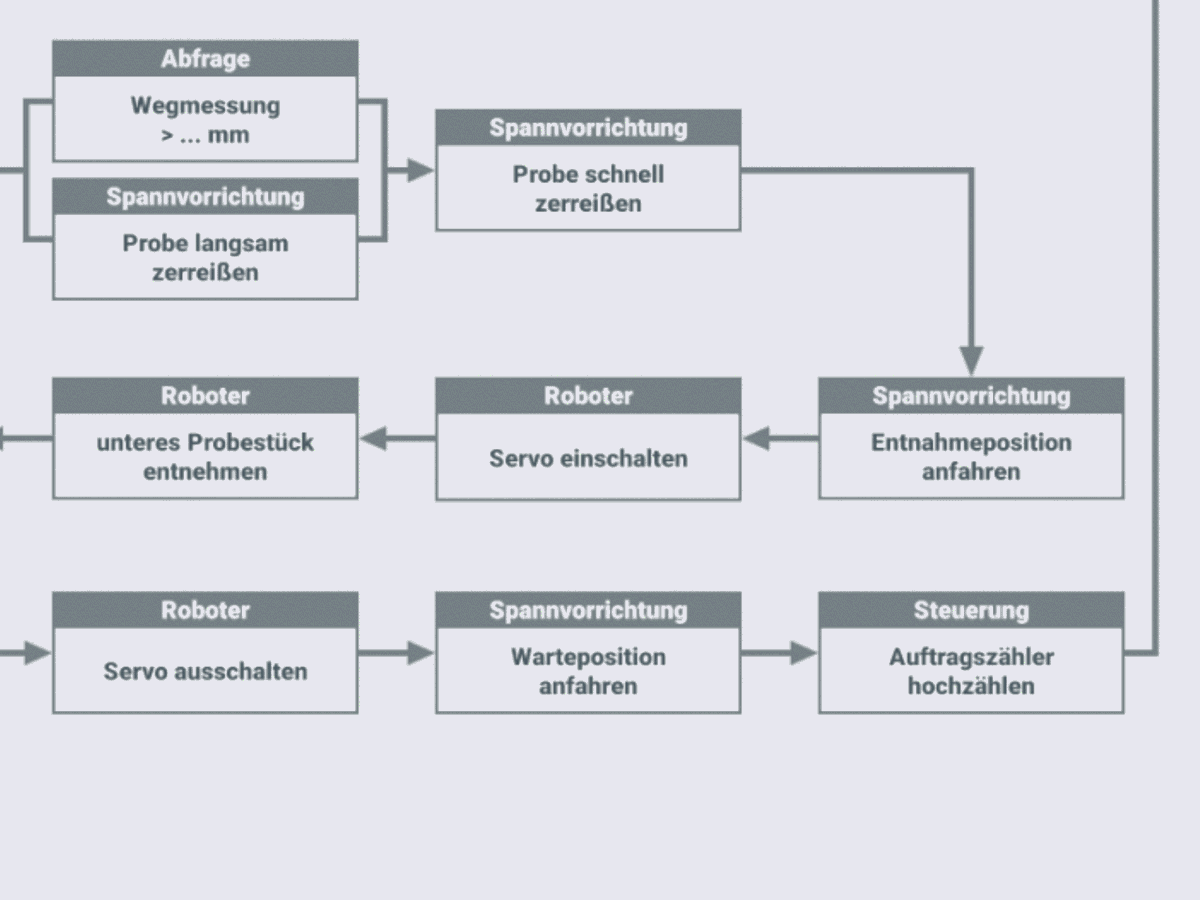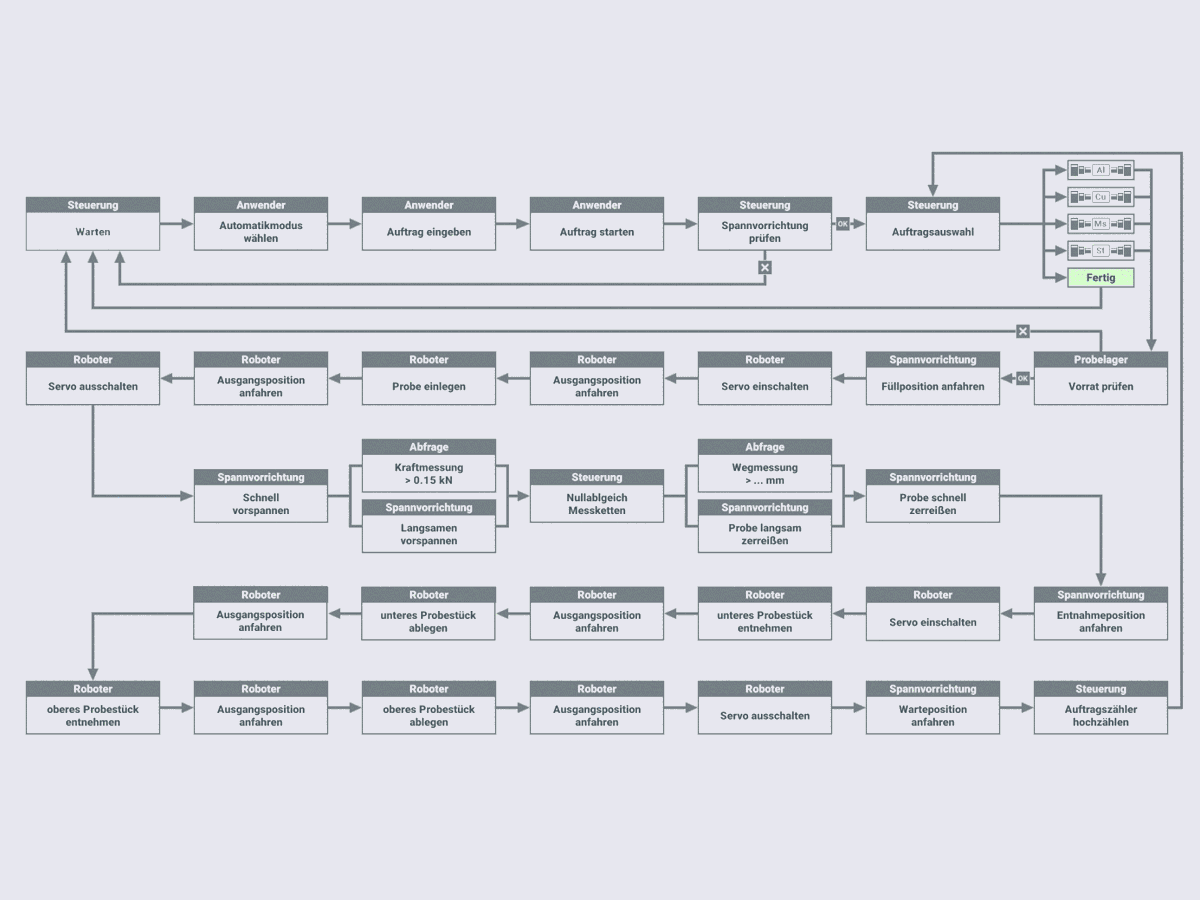
Automated procedure for recording stress-strain diagrams under standard conditions
 Smart communication
Smart communication
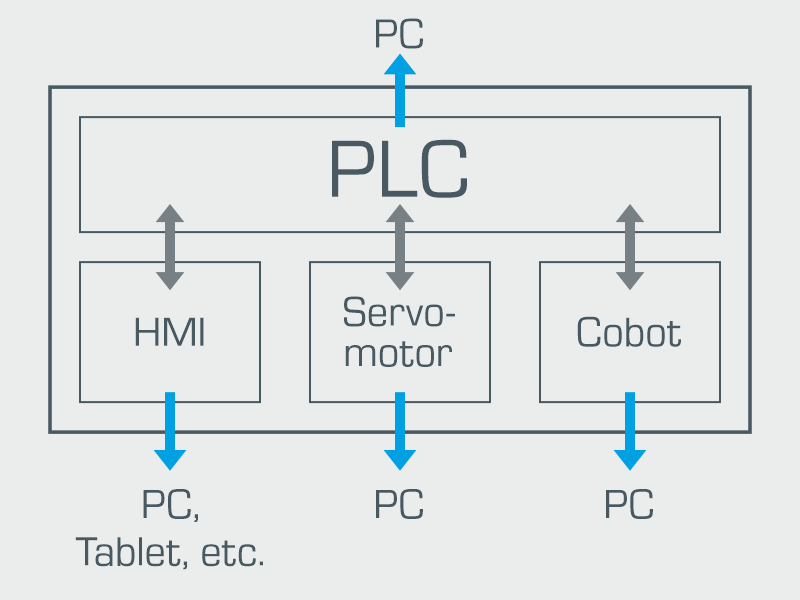
Communication topology: smart communication between actuators/components
 Low-code functions
Low-code functions

Low-code functions for creating automation scripts
 Programming
Programming
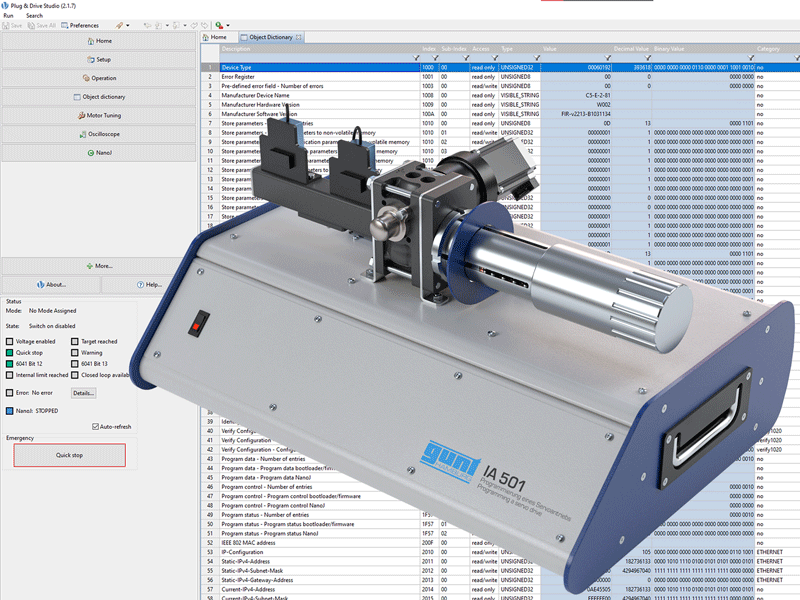
IA 501 can be used to program the motor controller for drive control
GUNT Skills Media Center
As a digital platform, the GUNT Media Center provides enormous added value and expands the use of the training systems.- manuals
- circuit diagrams
- worksheets and solutions
- user videos
- original documents from the component manufacturers

» Find out more
How is a process automated?
1. Process analysis
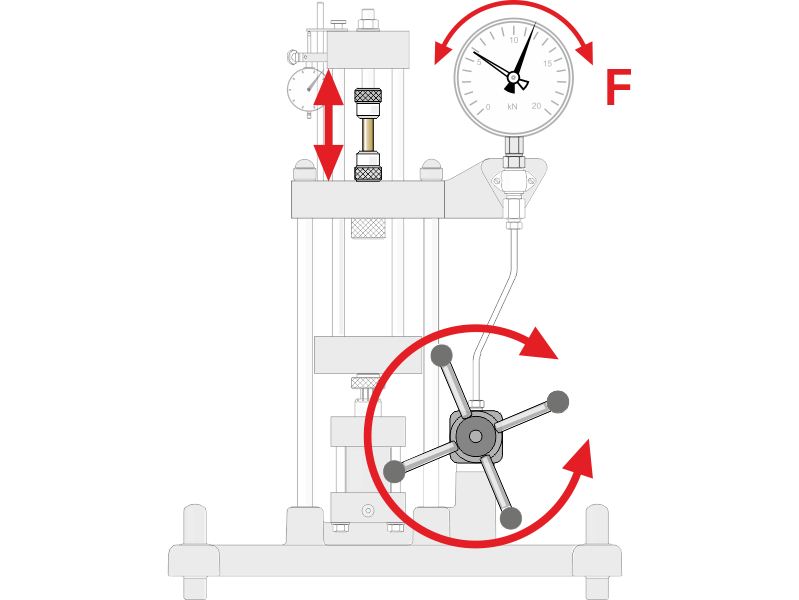
Analysis and identification of the process: the work steps are identified using WP 300.
» further information2. Concept creation
Development of a concept that defines the work steps, the required tools and the goal of automation. The process sequence is worked out in a flow chart.
» further information3. Implementation
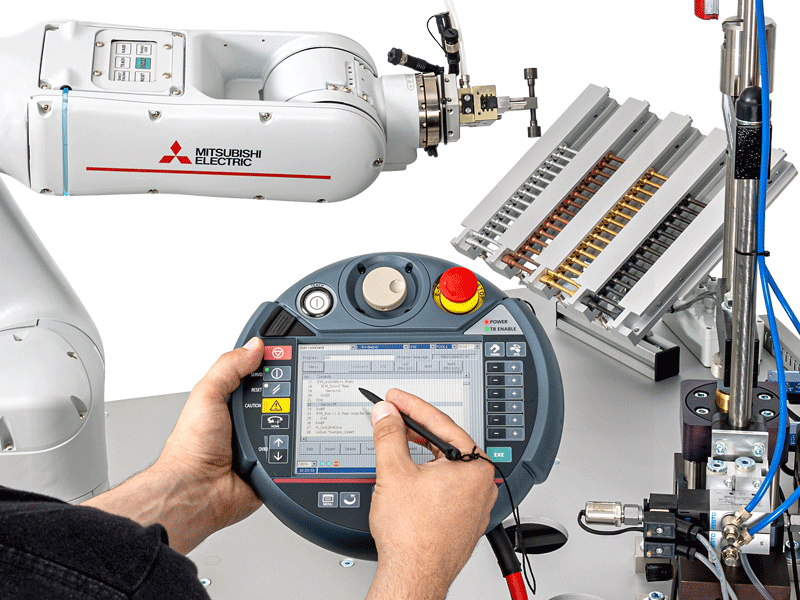
Implementation of the automation concept and programming of the cobot using the controller, analogous to the process sequence from the flow chart.
» further information4. Test and optimisation

- review of the operation and results of automation
- make appropriate adjustments if necessary
1. Process analysis

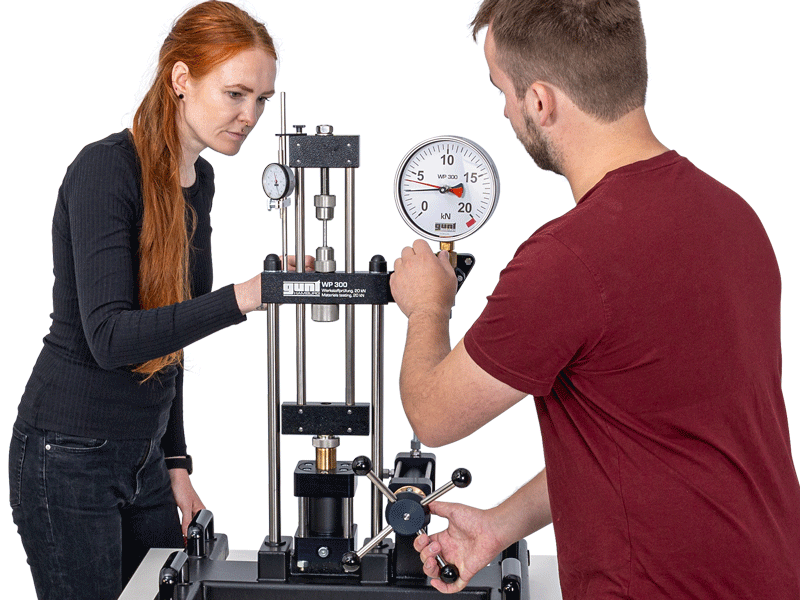
The work steps are identified using the manually operated materials tester WP 300, e.g.
- describe the system
- familiarisation with the tensile test
- recognise potential for automation
- develop solutions for movements
- define interfaces
Selection of specimens
Which material?
Different alloys?
What specimen geometry?
How long?
How are the specimens stored?
Clamping the specimen
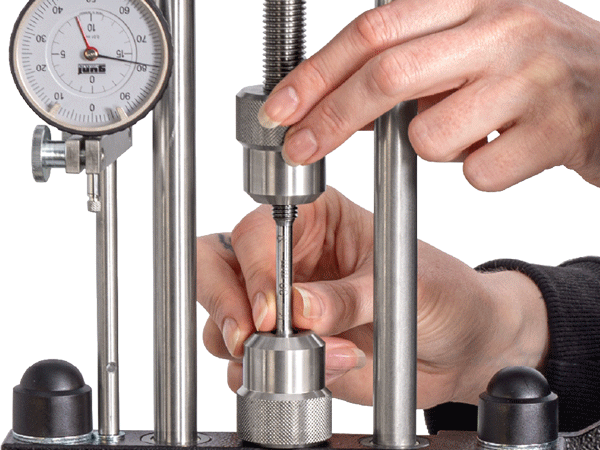
Which work steps are carried out manually, such as clamping the specimen, and which can be automated?
Applying force
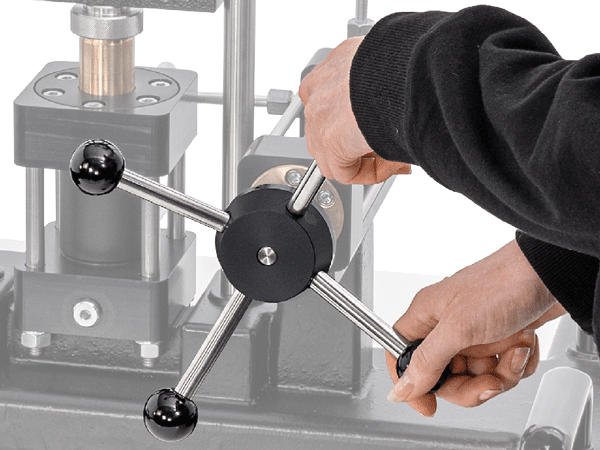
How is the specimen lengthened?
What happens if the specimen breaks? Which mechanical devices are required?
For example, the force is manually transferred to the clamped specimen using the handwheel.
Movements on the device
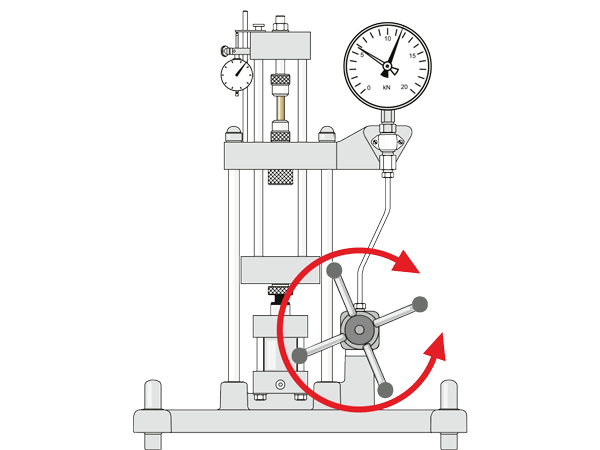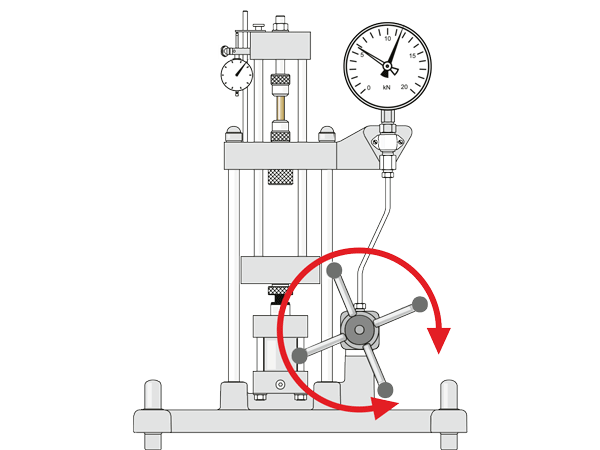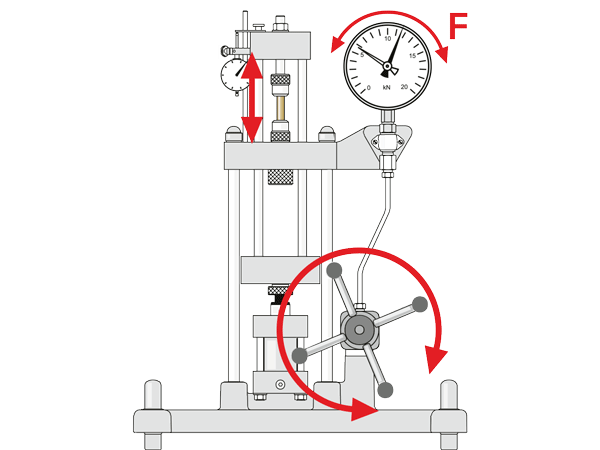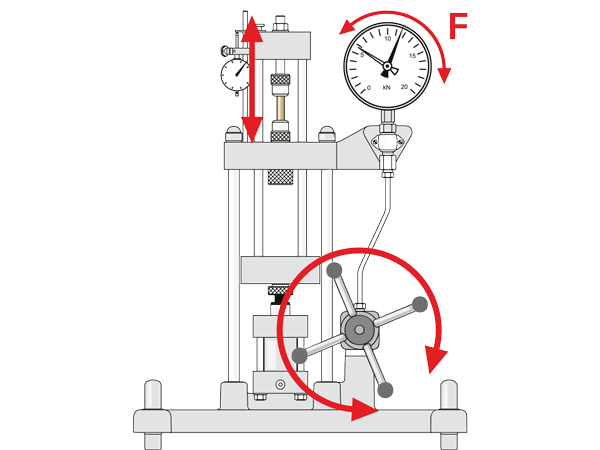
Which elements move?
What are the effects of the movements?
Identification of the fixed elements, the movements and their effects using the example of the WP 300 experimental unit.
2. Concept creation

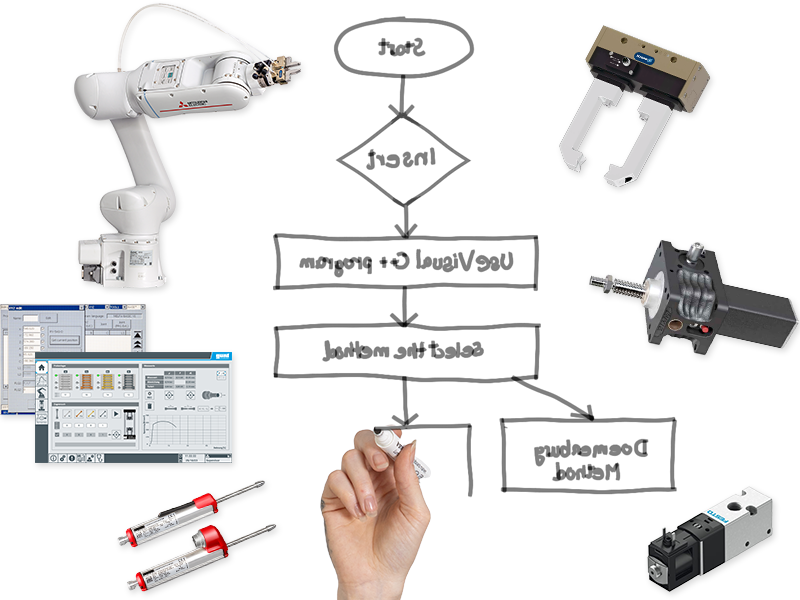
Development of a concept that defines the work steps, the required tools and
the goal of automation:
- create a sequence plan
- implementation in a flow chart
Possible selection of tools:
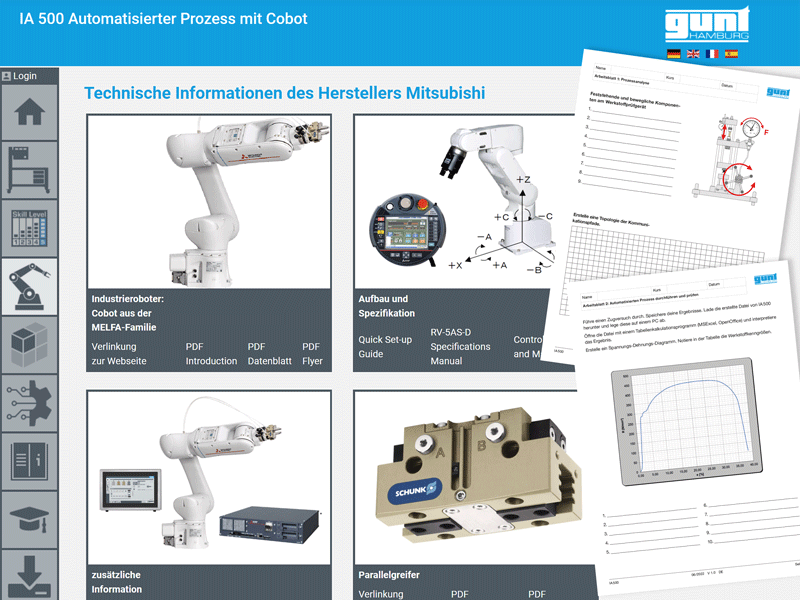
- industrial robot, e.g. from Mitsubishi
- gripper, e.g. from Schunk
- gear, e.g. from Zimm
- drive, e.g. from Nanotec
- pneumatics, e.g. from Festo
- sensors, e.g. from OPKON
- PLC, e.g. from Siemens
- etc.
» to the product IA 500 Automated process with cobot
3. Implementation

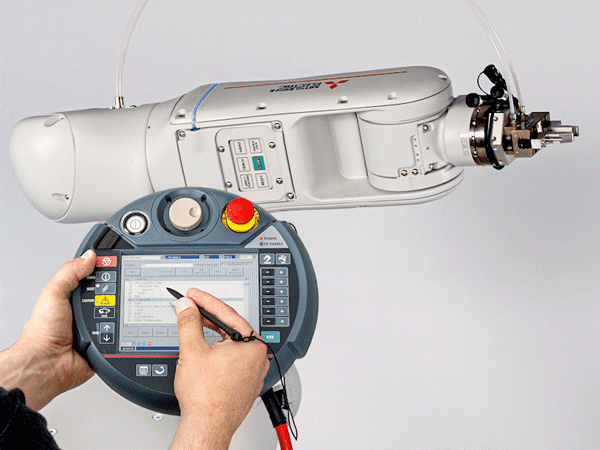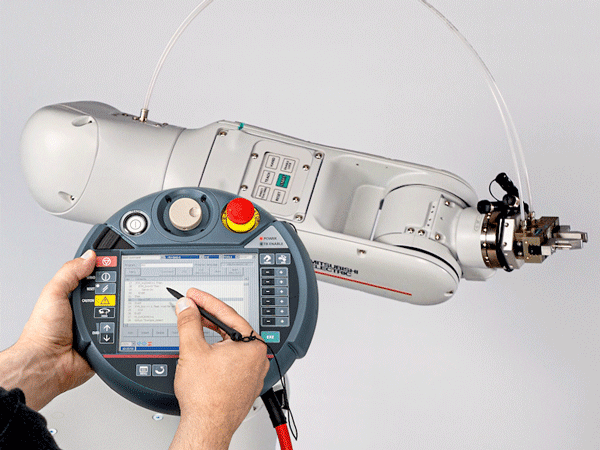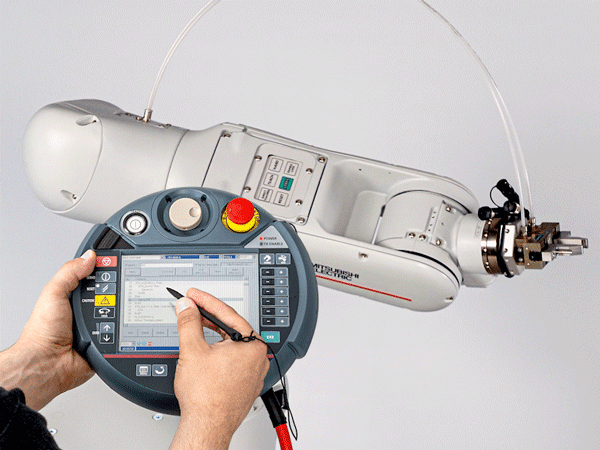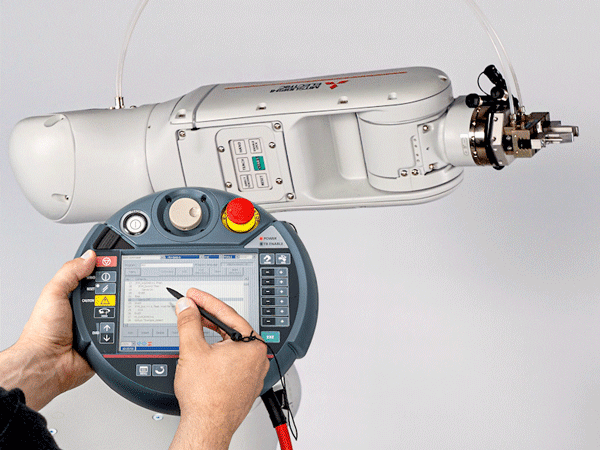
Implementation of the automation concept
Programming the cobot with the controller in IA 500
- teach the cobot
- define the working coordinates by saving points in the room
- determine pick-up and set-down points in the operating area
- etc.

Implementation of the automation concept
Programming the servo drive with IA 501
A small training device with a great learning effect:
- structure, function and programming of a servo drive
- targeted learning, completely independent of the large IA 500 system
» to the product IA 501 Programming a servo drive
4. Testing and optimisation

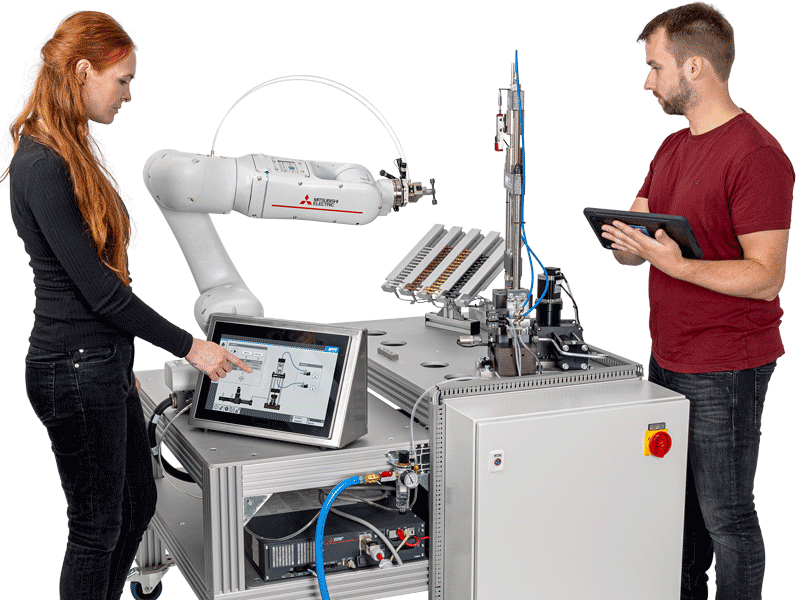
Commissioning, testing and improving
- carry out the automated process in which the complete tensile test is executed
- adaptation of paths and travel speeds
- check that the hydraulic systems clamp the tensile specimen and apply the tensile force to the specimen
- check the communication of all systems involved
- etc.
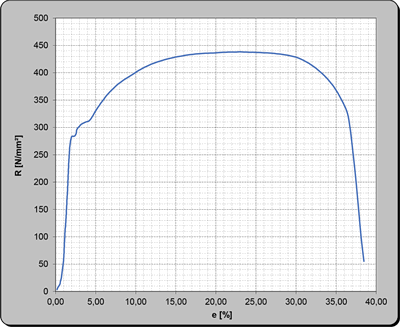
Complete process flow
Download