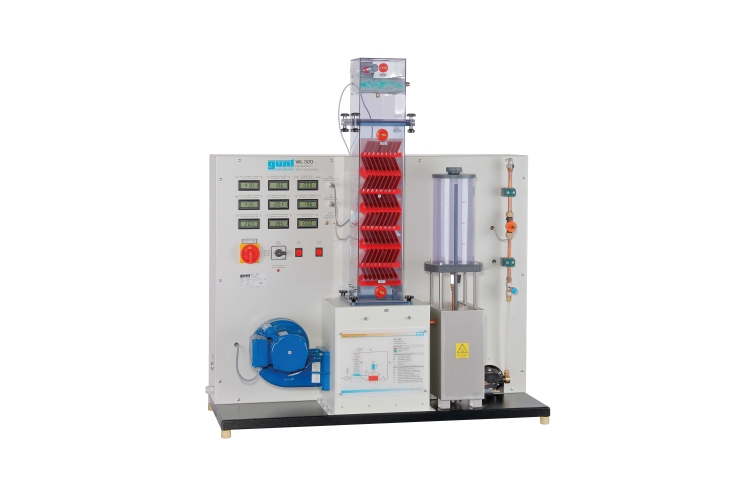
Wet cooling towers are a proven method of closed-circuit cooling and heat dissipation. Typical areas of application are: air conditioning, heavy industry and power plants.
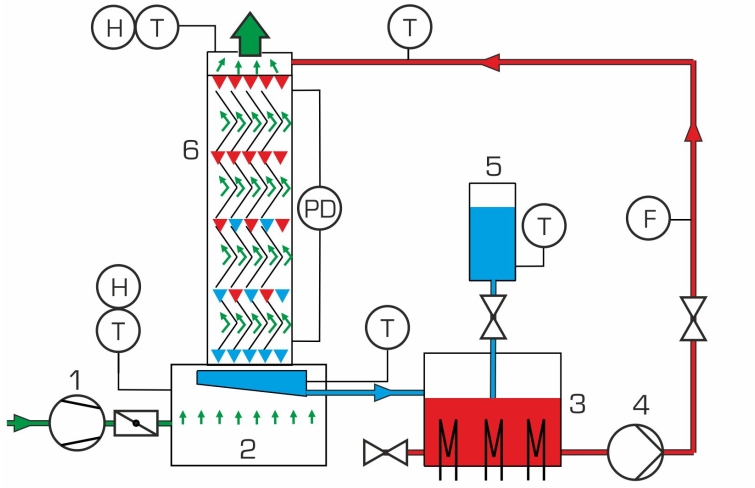
In wet cooling towers the water to be cooled is sprayed over a wet deck surface. Water and air come into direct contact in the counterflow. The water is cooled by convection. Some of the water evaporates and the evaporation heat removed further cools down the water.
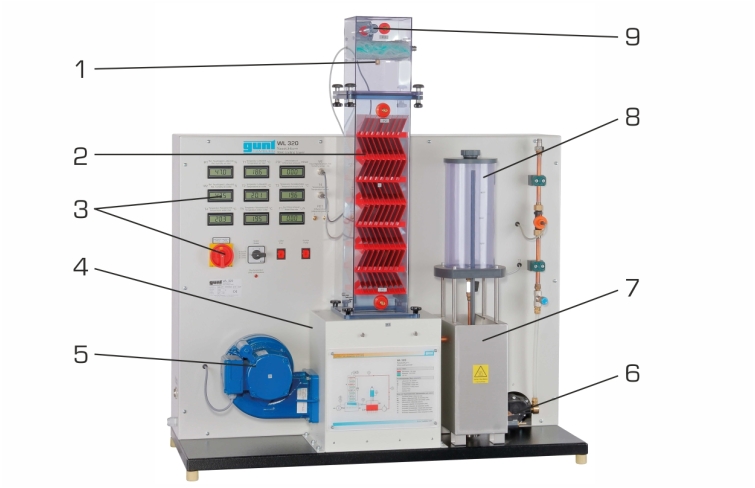
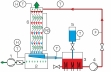
WL 320 examines the main components and principle of a wet cooling tower with forced ventilation. Water is heated in a tank and transported by a pump to an atomiser. The atomiser sprays the water to be cooled over the wet deck surface. The water trickles from the top to the bottom along the wet deck surface whilst air flows from the bottom to the top. The heat is transferred directly from the water to the air by convection and evaporation. The evaporated water volume is recorded. The air flow is generated by a fan and adjusted using a throttle valve.
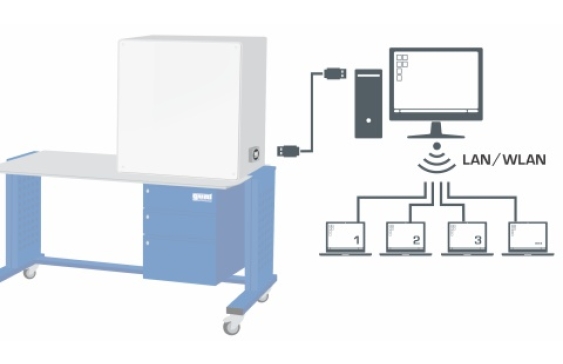
The cooling column is transparent allowing clear observation of the wet deck surface and the trickling water. Interchangeable cooling columns (WL 320.01 – WL 320.04) enable comparative studies.GUNT software for data acquisition via USB under Windows 10
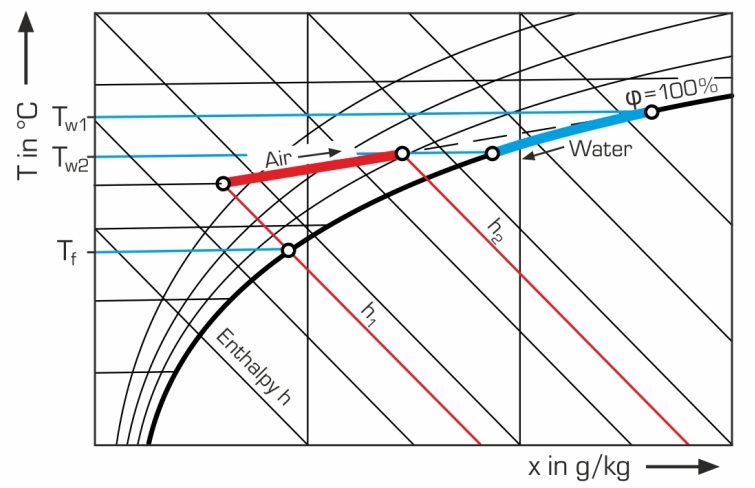
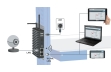
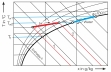
All important process parameters are recorded (volumetric air flow rate, temperatures of air and water, air humidity, water flow rate). The measured values can be read on digital displays. At the same time, the measured values can also be transmitted directly to a PC via USB. The data acquisition software is included. The changes of state of the air are represented in an h-x diagram.