Pressure losses occur during the flow of real fluids due to friction and turbulence (vortices). Pressure losses occur in pipes, pipeline elements, fittings and measuring devices (e.g. flow meters, speedometers). These pressure losses must be taken into account when designing piping systems.
HM 150.11 allows to study the pressure losses in pipes, piping elements and shut-off devices. In addition, the differential pressure method is presented for measuring the flow rate.
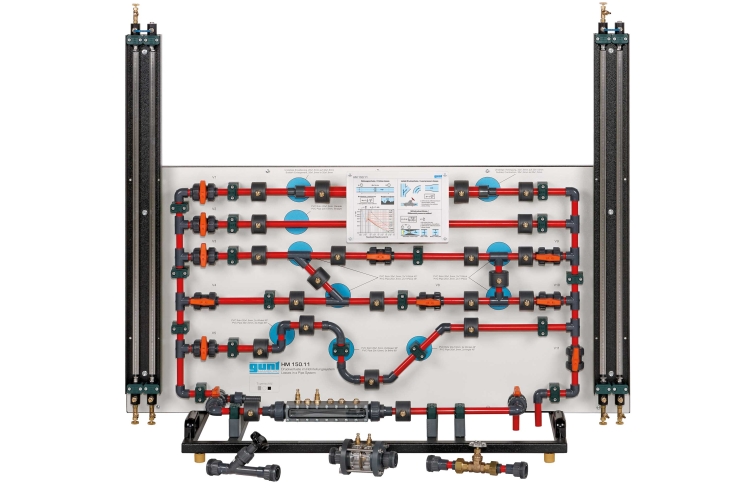
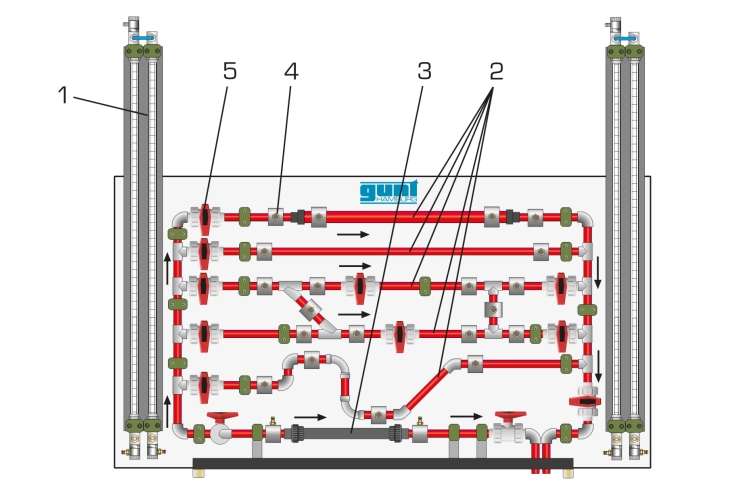
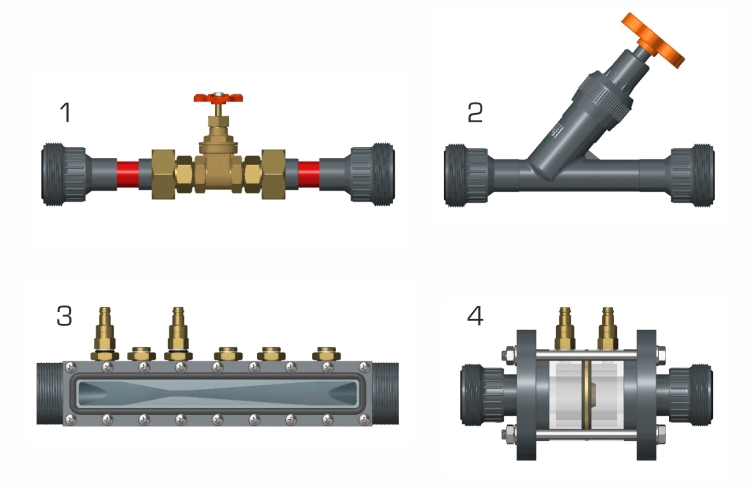
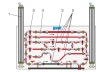
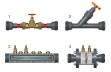
The experimental unit contains six different pipe sections capable of being shut off individually. The pipe sections are equipped with piping elements such as bends, elbows and branches. In one pipe section, different shut-off devices and measuring objects are installed to determine the flow rate. The measuring objects are made of transparent material and provide excellent insight into the inner structure. The pressure measuring points in the piping system are designed as annular chambers. This creates a largely interference-free pressure measurement.
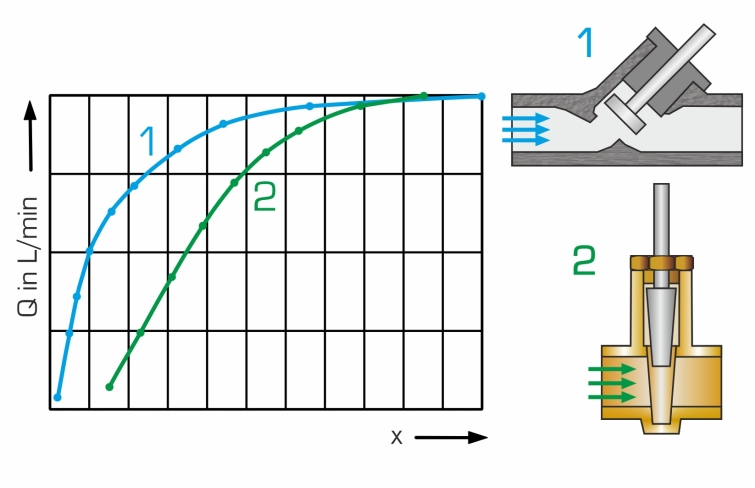
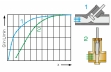
The experiments measure the pressure losses in pipes and piping elements, such as branches and bends. The opening characteristic of the shut-off devices are also recorded. The pressures are measured with twin tube manometers.
The experimental unit is positioned easily and securely on the work surface of the HM 150 base module. The water is supplied and the flow rate measured by HM 150. Alternatively, the experimental unit can be operated by the laboratory supply.