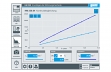
In the continuity equation, the relationship between the cross-sectional flow area and the flow velocity is analysed. These physical laws are the foundation of fluid mechanics.
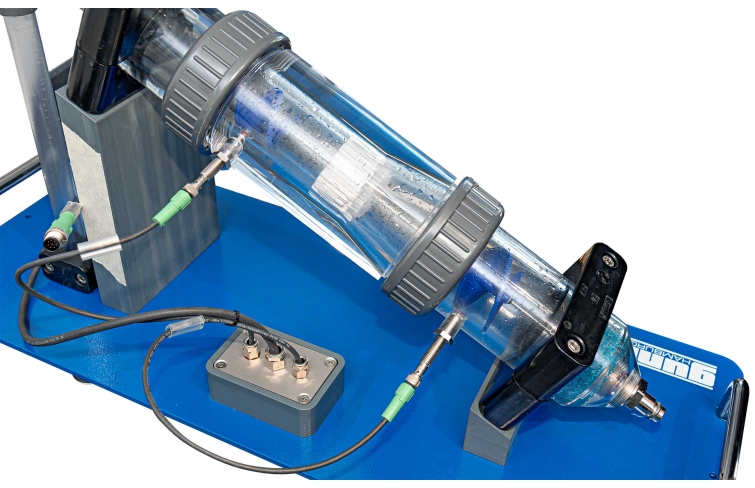
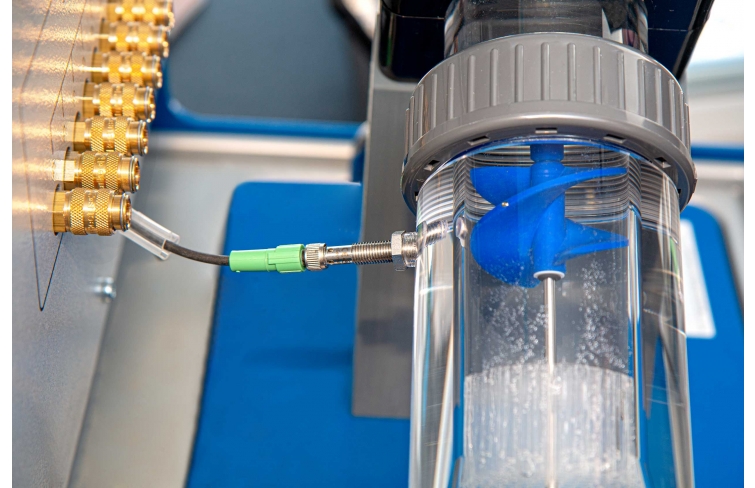
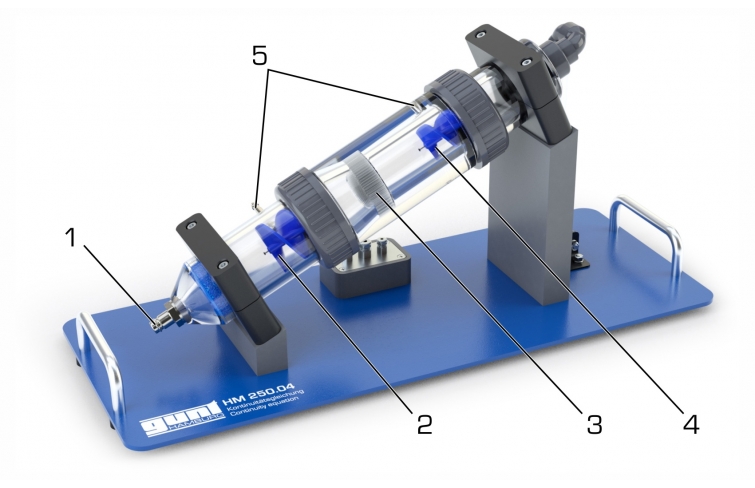
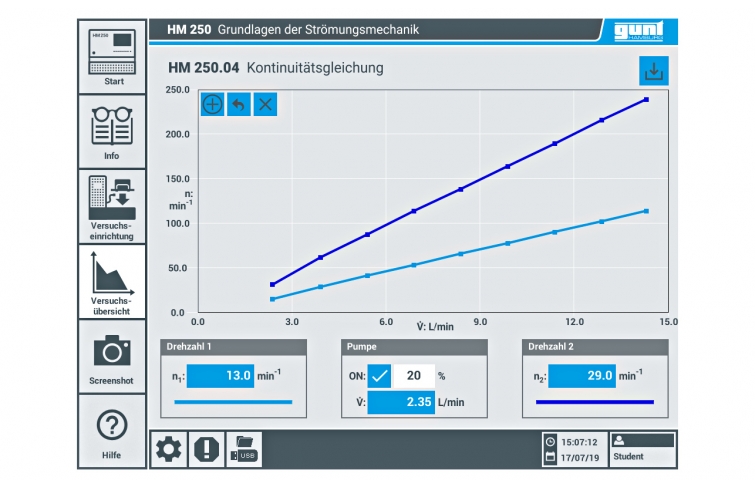
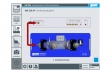
HM 250.04 consists of a transparent pipe section with a change in cross-sectional area. To measure the flow velocities in the two different pipe cross-sections, the pipe section contains two impellers with the same pitch. In the experiment, the impellers are rotated by the flowing water. The change of cross-sectional area in the pipe section leads to a change in the flow velocity. The speed of the impellers is proportional to the flow velocity. The speeds, and thus the flow velocities, are recorded inductively. Since the geometry of the two pipe cross-sections is known, it is possible to establish and check a ratio of the speeds. Variances between theory and practice are discussed and limits to implementation are pointed out.
The impellers cover a large part of the flow area, so that irregularities in the flow are largely compensated. During the experiment, incompressible flow is present due to the use of water as working medium. Therefore changes in density do not have to be considered.
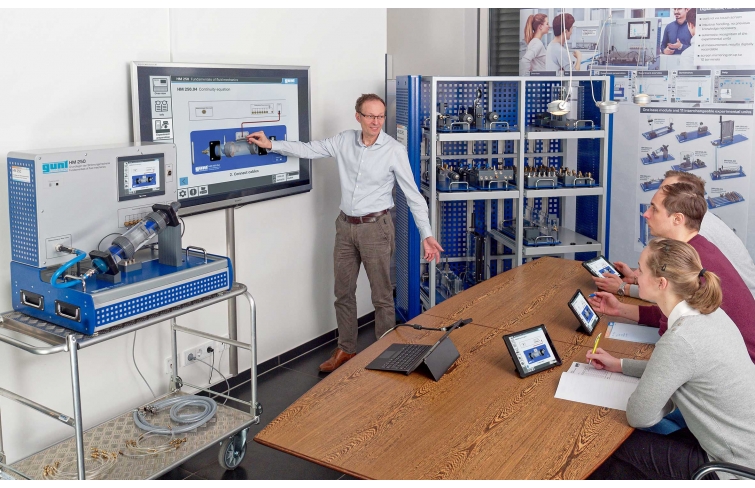
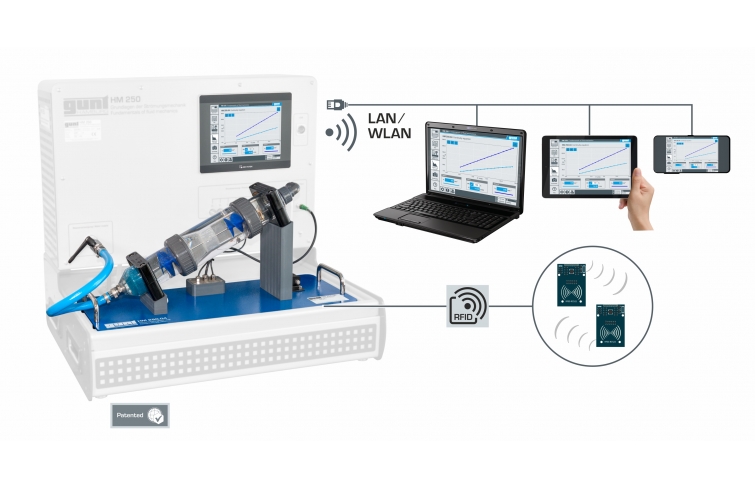
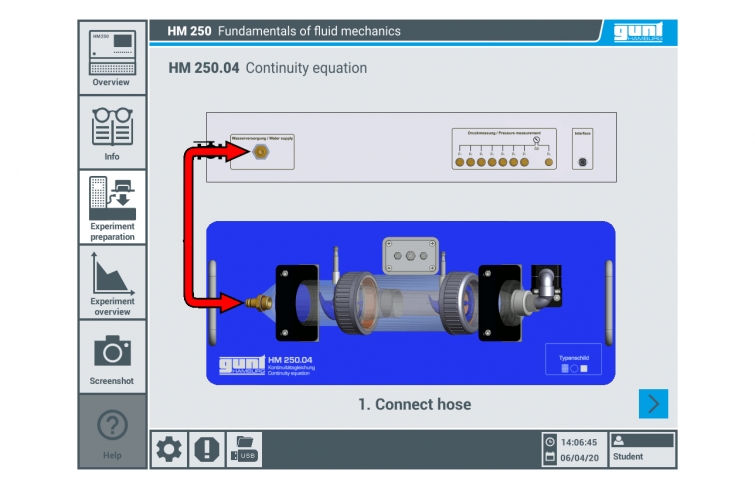
The accessory HM 250.04 is positioned easily and securely on the worktop of the HM 250 base module. Via RFID technology the accessories are automatically identified, the appropriate GUNT software is loaded and an automatic system configuration is performed. The intuitive user interface guides through the experiments and displays the measured values graphically. For tracking and evaluation of the experiments, up to 10 external workstations can be used simultaneously using the local network via LAN connection. The base module supplies the water and is used to adjust the flow rate. Flow rate measurement is also carried out via the base module.