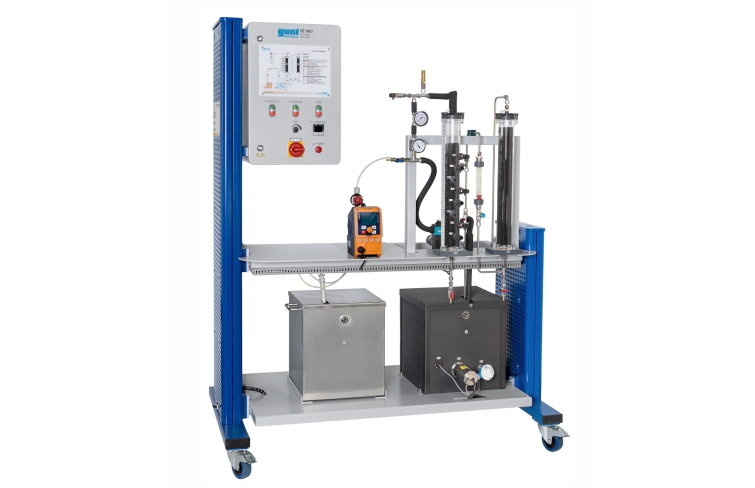
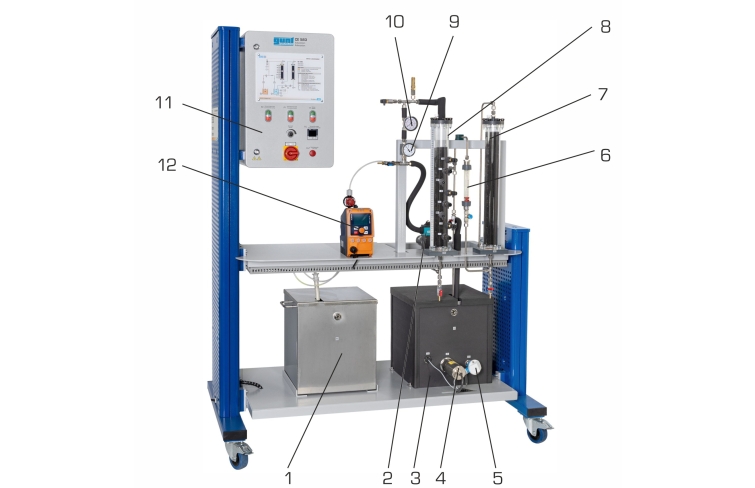
CE 583 demonstrates the removal of dissolved substances by adsorption. During adsorption the substances dissolved in the raw water are called adsorbate.
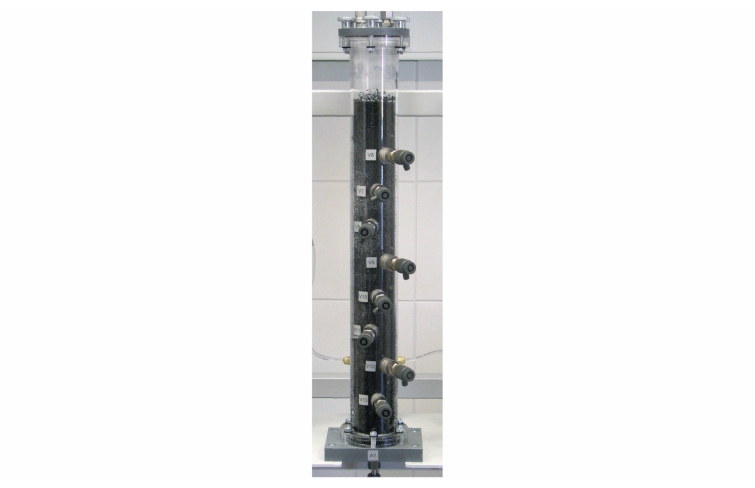
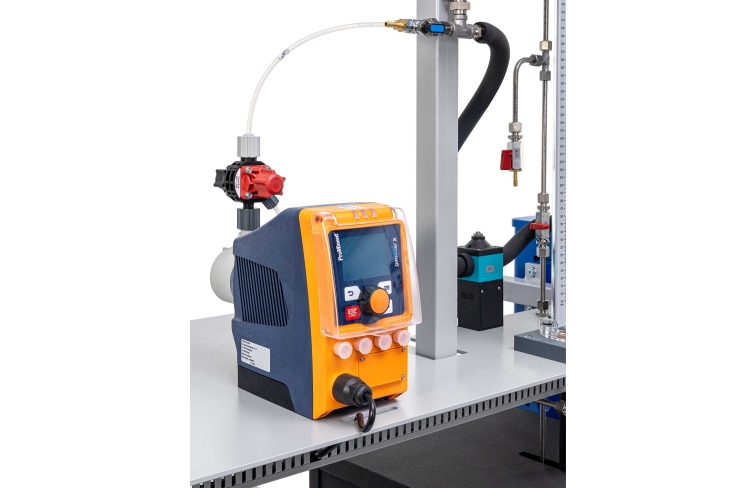
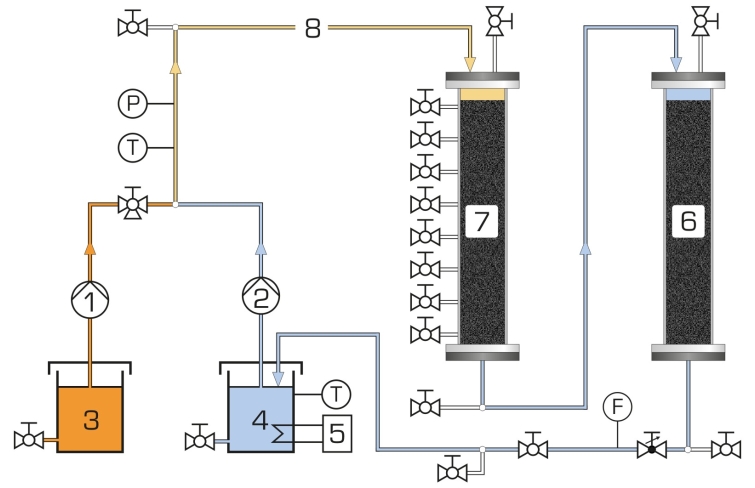
A pump transports the water from a tank in a circuit with two adsorbers filled with activated carbon. The pump transports treated water to the first adsorber. A concentrated adsorbate solution is added to the treated water flow using a metering pump. The raw water produced in this way enters the adsorber and flows through the activated carbon fixed bed. Here the adsorbate adsorbs on the activated carbon. To remove any quantities of adsorbate still present from the water, the water then flows through a second adsorber (safety adsorber). The treated water is returned to the feed line of the first adsorber where concentrated adsorbate solution is added once again. This creates a closed water circuit.
The flow rates of both pumps can be adjusted. Thereby the following parameters can be varied:
- concentration of the adsorbate in the raw water
- contact time of the raw water with the activated carbon
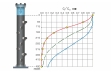
The water temperature can be controlled. This allows for the temperature effect of the adsorption to be investigated. Flow rate, temperature and pressure are continuously measured. Sampling points are arranged in such a way that breakthrough curves and concentration profiles can be plotted.
Analysis technology is required to evaluate the experiments. The choice of analysis technology depends on the adsorbate used. Methylene blue can e.g. be used as adsorbate. The concentration of methylene blue can be determined using a photometer.