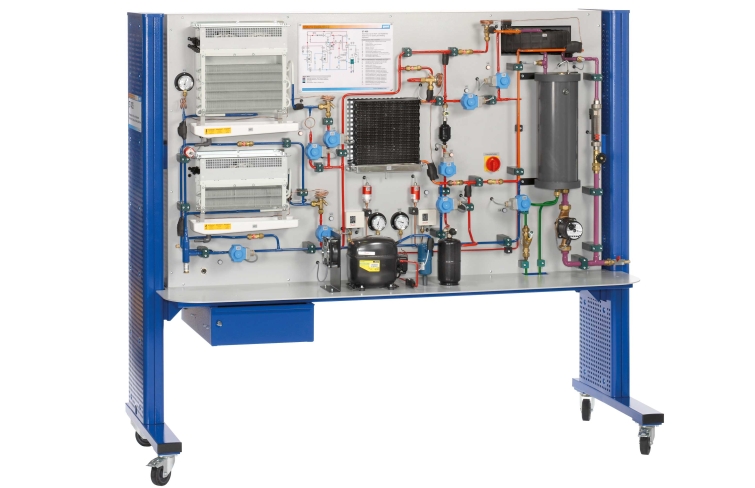
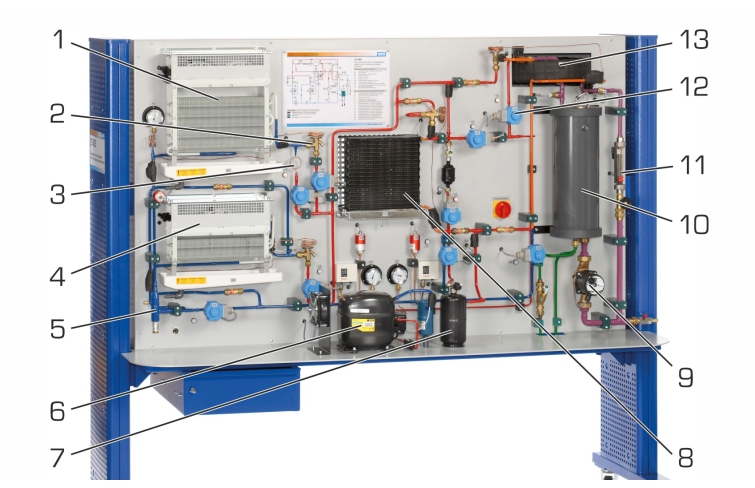
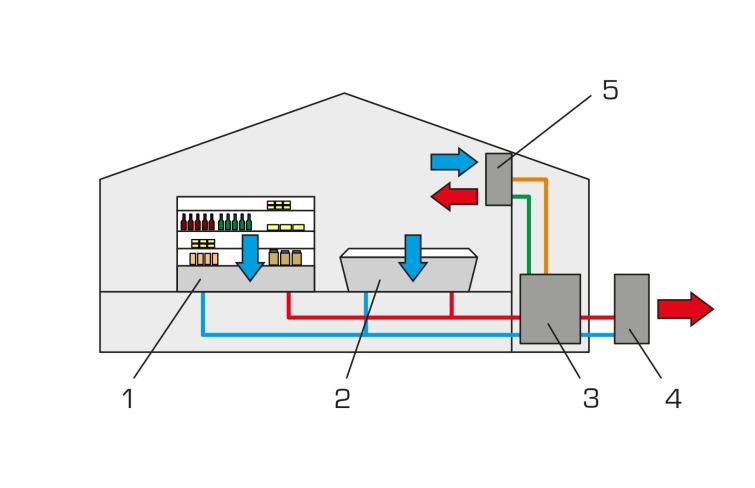
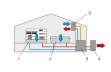
Refrigeration systems and heat pumps only differ in the definition of their use, but can be of the same design. For example, goods can be refrigerated in a supermarket and the store heated with the waste heat. The store can also be cooled with the same system in the summer.
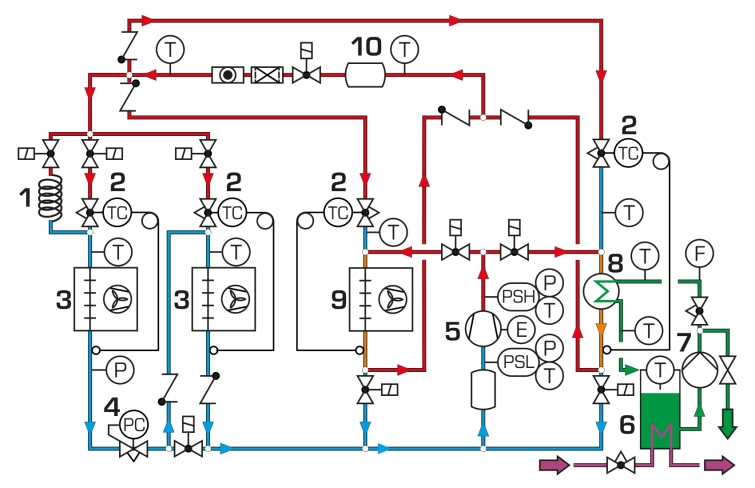
With ET 405 the cooling and heating operation can be investigated. Different operating modes can be set via solenoid valves.
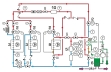
The refrigeration circuit with compressor and condenser (heat exchanger with fan) includes two evaporators with fans (refrigeration stage and freezing stage) and thermostatic expansion valves. The two evaporators can be connected in parallel or in series. For the connection in series the capillary tube serves as expansion element for the refrigeration stage evaporator. The refrigerant circuit is connected to a glycol-water circuit via a coaxial coil heat exchanger. Via solenoid valves the coaxial coil heat exchanger can be switched as an evaporator or condenser. Thus the glycol-water mixture in the tank can be heated or cooled. In pure cooling operation (without heating function) the heat exchanger with fan as air-cooled condenser dissipates the heat. This heat exchanger can be also switched as an evaporator. The different operating modes can be selected in the GUNT software supplied.
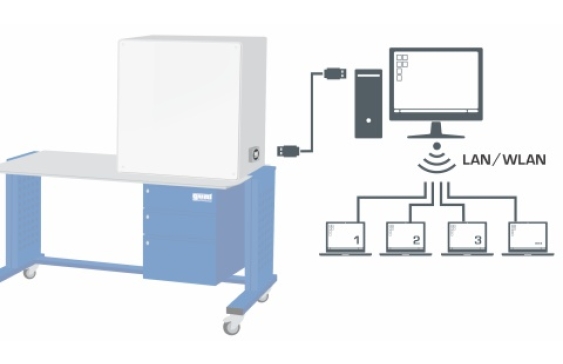
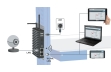
The measured values are transmitted via USB directly to a PC and displayed there. The GUNT software enables easy analysis and the representation of the process. In addition, the GUNT software provides exact data on the condition of the refrigerant, which is used to calculate the refrigerant mass flow rate accurately. The calculation therefore gives a much more accurate result than measurement using conventional methods.