With the increasing demand for refrigeration worldwide, the interest in processes of cold production which can be supplied from renewable energy sources is also growing. The use of solar electricity offers particular advantages for mobile and very remote applications.
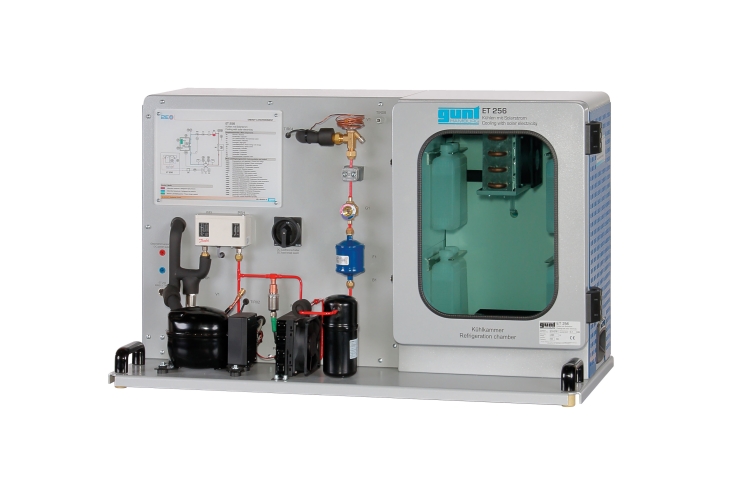
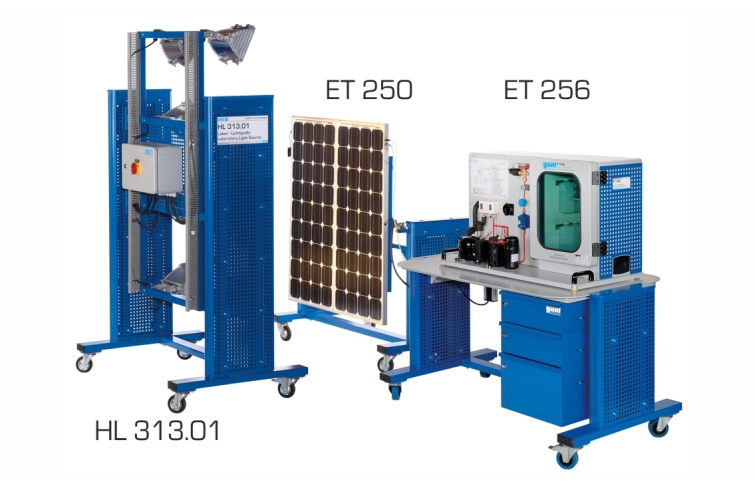
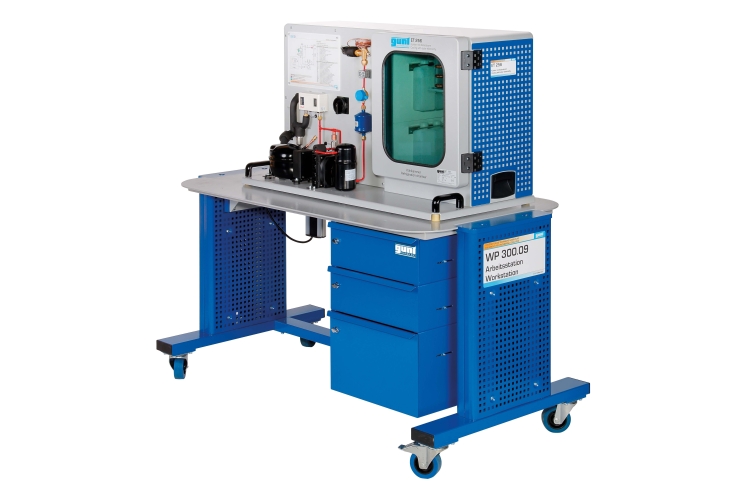
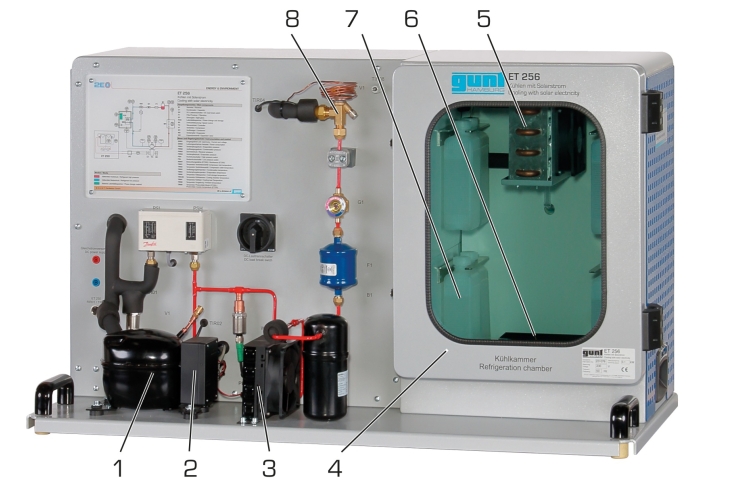
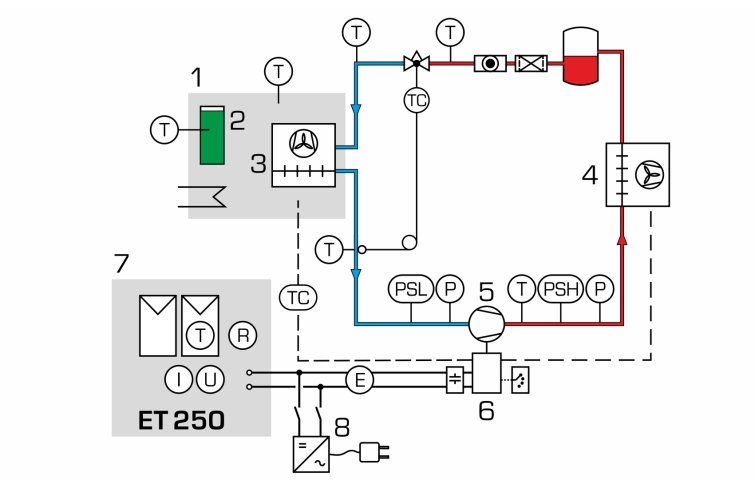
ET 256 contains a typical compression refrigeration system with refrigeration chamber. It is possible to supply the refrigerant compressor directly with current from photovoltaic modules. To do this, the photovoltaic modules from ET 250 are connected to ET 256. For some experiments, the laboratory power supply ET 256.01 can also be used. The artificial light source HL 313.01 enables solar energy experiments independently of natural sunlight.
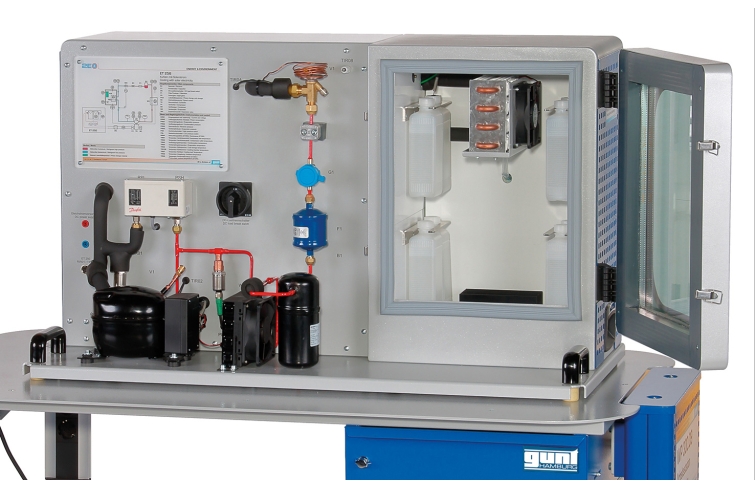
The refrigerant compressor is a piston compressor with adjustable speed. A thermostatic expansion valve is used in the refrigeration circuit. The insulated refrigeration chamber contains a refrigerant evaporator with fan, removable cold accumulator and a heater for generating a cooling load.
For cooling, the compressor is started by the control unit when sufficient electrical power is available from the solar modules. Operating the compressor reduces the temperature in the refrigeration chamber. Should the cold accumulators be fully or partially discharged, they are charged again as soon as sufficiently low temperatures are reached. If there is no current available to operate the compressor, the cold accumulators increase the remaining cooling time in the refrigeration chamber and are discharged in this way.
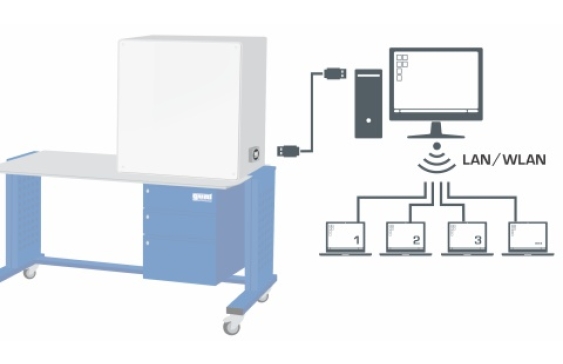
Relevant measured values are recorded by sensors, displayed and can be processed in a PC. The GUNT software provides exact data on the condition of the refrigerant, which is used to calculate the refrigerant mass flow rate accurately. The calculation therefore gives a much more accurate result than measurement using conventional methods.